Development Process of Computer-Based Training (CBT)
CBT Execution Plan
- What inputs do we need to make Computer Based Training?
All approved documents softcopies, Images, Videos, and 3D Models.
- When will you start the work?
On the same day when we receive all Final softcopies.
- What is the duration required to develop Computer Based Training?
3 hours output per 25 Working Days after Approval of Storyboards and scripts.
Now, let us Know the Process of Computer Based Training Execution.

Services
Computer-Based Training (CBT) Execution Process
Raw Content & TOC
Client Scope
- The Client must share all the Raw files (PDF files, Word files,3D Models, Images and Videos) with the topics listed in the scope document.
- A client has to share the Table of contents with the topics to be covered in Computer Based Training
Script: Code and Pixels
Our Instructional Designer team will prepare the draft script of the Raw Document and we will share the script for approval.
Story Board (Code and Pixels)
- After doing additions/deletions/updation and approval of the script by the Client, a draft storyboard will Developed by Our ID Team.
- Storyboard will consist of the Proposed graphic user interface, button structure, content hierarchy, navigation sequence and presentation method i.e. whether the screen is explained using 3d View, 3D Animations, 2D Animations, Graphics, Line drawing, Images, Videos etc.
Approval
Client
- Storyboards will be Delivered to the Client after our Internal QC for Review.
- Data Correctness and Technical Content or Process to be verified and Approved by the Client.
Videography
Computer-Based Training (CBT) Development Process | Code and Pixels
Code and Pixels and Client Subject Matter Expert
- After approval of the Storyboards, the Videography schedule is planned.
- Based on instructions available in Storyboard, The Videography team will capture all the inputs required for the development of Computer-Based Training.
Alpha Version: Code and Pixels
- Graphic Designer Team Will Develop the CBT Content Based on the instructions available in the Storyboard.
- After Deployment of the Content and Performing QC an Alpha Version is released to Client for the Review.
Beta Version
After obtaining the Review Comments from the Client updations will be done if Required and a Final Version will be Released and Delivered to the Client.
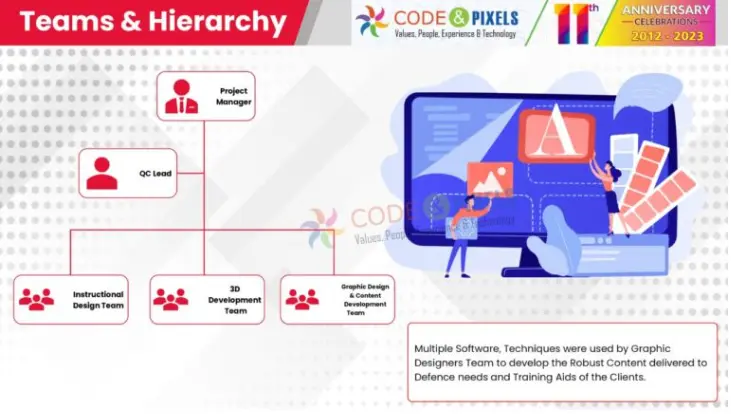
Teams & Hierarchy – Project Manager
The CBT project will be managed by a project manager, who will be in charge of gathering the necessary client input, project execution, quality control, review, and final CBT delivery to the client.
QC Lead: QC Lead will be Assigned to Perform the Reviews of Storyboards, Content Development and Final Output. QC will be performed in every step of the CBT Development Process.
Instructional Design Team: The team responsible for instructional design will work on pre-production tasks such as scripting, storyboard development, voice-over, knowledge transfer, animator instructions, technical clarifications, and alpha quality control.
CBT 3D Graphic Design & Content Development Team Code and Pixels
3D Development Team
For the purpose of explaining the procedure and highlighting the many components, the 3D team will produce the 3D models of the system, including texturing, lighting, animation, and rendering.
The use of 3D animation will assist in clarifying processes using animations that are not feasible to display in real-time. By creating high-level technical animations, 3D animations may also be used to depict internal processes.
Graphic Design & Content Development Team
In both the production and post-production phases, the graphic design team will integrate 3D animation, images, videos, and 2D graphic content making use of the approved storyboards and directions provided by the ID team.
The graphic design team employed a variety of software and techniques to create robust content that met the demands of the defence industry and the clients’ training aids.
What are the details required to make CBT
Before starting CBT, OEM must finalize the duration of CBT. In some military RFP/SCOPE duration of CBT is mentioned along with the duration of each topic, subtopic, and sub–sub-topic.
If that is not mentioned then OEM has to make a Table of content first and mention the approximate time to cover each topic, subtopic, and sub–sub-topic.
It is called CCID, or course content Identified document. It is basically a full detailed Table of content and duration.
Once the CCID document is ready then, the Vendor will collect raw content and make a DCID document.
Which means a Detailed Course content document. It can also be called a storyboard. This storyboard will have complete content for every topic, subtopic, and sub–sub-topic.
Also, this document will contain the presentation methodology. It means is this particular sub-topic is being covered as Video, or Image, Text or animation if animation, 2d or 3d, etc.
Based on the number of words we can arrive at a number of hours.
If the number of hours is more than deliverable, we can concisely edit or delete unwanted text.
Once the DCDD is approved by end-user/ Army then we can start production of CBT.
Content Development Approach
Step -1 Shell/ Prototype/Template Design
The first step in the creation of the CBT is to design the functional prototype, branding, skinning i.e., the template of the course. This will be developed based on inputs like target audience, their skill/education level, nature of topics, other navigation facilities like
- play and Pause
- Forward, Rewind
- Audio mute, Audio control
- Seek bar
- Book mark
- Glossary
- Audio Transcription script
- Gallery
- Summary
- Reference
- Help
and prototype/ functional shell will be sent to the client for review and approval.
Step -2 Development of Design Documents
Based on the inputs provided by Subject Matter Experts (SME), a team of Instructional Designers will prepare a Table of Content / Course content identification Document and Storyboard/ Script/ Detailed Content Design Document consisting of the text that will appear on the screen. The corresponding text for voice-over, graphic design instruction will also be provided. Instructional Designers will interact closely with the SME and obtain the inputs, grasp the concepts, reproduce them as content, and finally get it reviewed by the SME/ Client.
The storyboard will be checked for technical, typographical, and grammatical errors. Checks will also be done to ensure that the content matches the requirements specified by the client. Errors found will be rectified and the final content will be sent to the client for approval and sign-off.
Our instructional designers develop design documents as per the guidelines of principles of adult learning, Instructional Design Taxonomies such as Bloom's Cognitive Taxonomy, Dick and Carey Model, Kemp's Instructional Design Model, Gagné's 9 Events of Instruction, Kirkpatrick's 4 Levels of Training Evaluation
Step -3 Approval of Design Documents
The client will review the Design Document, and pass back the reviewed document with Comments, suggestions if any
Step -4 Content/ Media/ Assets/ Development and Authoring
After the necessary Corrective Actions are implemented, the multimedia team will put together the approved template and the contents to create the complete version of the e-Learning course. Based on the storyboard, graphics and animations will be included at the appropriate locations to enhance the learner’s understanding of the points being discussed. Voice-over will be recorded as necessary, and the graphics and animations created will be synchronized with the text.
This developed version will pass through a series of stringent quality checks sent to the client for review and approval. This version is called Alpha Version
Sep -5 Beta Version
The client will review the Alpha version and pass back the reviewed content with comments, suggestions, etc. for corrections if any. Once these corrections are fixed by the Development team then once again the corrected Final version will be submitted to the client along with relevant approval documents
Step -6 Gold version
Gold version DVD contains the following multimedia elements
- Approved/ Final Table of Content
- Approved/ Final Design Document (Script, Story Board, Detailed Design Document)
- •Alpha Version
- Beta Version
- CD Version
- Raw contents (images, PDF, DOC, PPT, other files collected from client)
- User Manuals, Test Documents, Graphic Charter
- Quality Assurance Document
and prototype/ functional shell will be sent to the client for review and approval.
Code and Pixels Content Development Life Cycle (CDLC)
Putting the Code and Pixels Content Development Life Cycle (CDLC) in a simple way:
Our Project life cycle comprises 3 Phases i.e. Pre-project Analysis, Project Production, Post Project support.
Phase – 1 Pre Project Analysis
- Requirement Analysis
- Proposals & Quotation
- Approval
Phase – 2 Project Production
1) Pre Production:
- Detailed client requirement analysis, Collection of raw material, Project Planning
- Table of Content/Course Specific Document/Course content Identification Document
- Script/Story Board/ Visual Story Board/Detailed Content Design Document
- Quality Check
2) Production:
- Videography, Photography, Voice Recording
- Development of Graphic Assets, Animations, Programming, Integration, Internal QC
3) Post Production:
- Quality Check and Delivery of Alpha/Beta/Gold Versions
- Media Generation / Content Deployment / Delivery
- Training to users/ facilitators
Phase 3 – Post Project Support
In addition to providing superior E-content, we provide Post Project Support to the client. We conduct feedback analysis sessions from different actual users and collect user feedback on the project/ content so that we can augment the content next time. The best way to improve the usability of the content is to address the critics of the content.
LEVELS OF CBT
Level 1. Passive-no interaction
This level is what is commonly referred to as ‘page-turners'. The course is linear and could be considered basic training, in which the student acts only as an information receiver.
Basically, the sequence of screens is fixed and the student can not choose the order in which you want to see the content, return to a previous topic or browse freely. However, it can be effective for communicating simple concepts
At this level learners do not interact with resources, they just have:
- Graphics, images
- Rollovers
- Basic quiz questions
- Some refer to level 1 e-learning as the “click next” style of e-learning. It has very low amounts of interactivity (i.e., clicking the Next button is as interactive as it typically gets) and there is a lot of static text and images.
- Level 1 quizzes are usually basic multiple-choice and true-or-false questions. Level 1 e-learning, while basic, does have its place: it can be a quick and inexpensive way to cover simple rules or procedures.
- These types of courses or CBTs are used for classroom teaching
- No Or very minimal Voice over is used
- Power point-based course development
Level 2. Limited interaction
In this case, the course continues to be basic, but the student has more control over their training; they can do more than just watch, read and navigate. This level is used for non-complex operations and maintenance lessons.
- At level 2, e-learning courses start to have multimedia. Courses at this level typically contain some audio and video, as well as some basic animations and transitions. This level of content is also often accompanied by narration and activities such as “click and reveal” interactions.
- Typical level 2 quizzes are drag-and-drops and matching activities.
- Level 2 e-learning is often used because it’s a nice middle ground that offers a richer experience for the learner
- At this level, learners interact with resources such as:
- Clickable animated graphics
- Navigation expands to menus, glossaries, and links to external resources.
- Often includes simple exercises (i.e. drag-and-drop, matching, and identification components). Audio and video.
- This level is best for courses that are intended to support on-the-job-performance or when importance is more on the skill development
- (Software simulations using Demo, Practice, Perform/Hands-on) , video documentaries real-life scenarios, etc.
This level is a favorite in the industry mainly because it optimized the balance between active learning and development time.
Level 3. - 3d, Character animations or high-level Technical Animations
This level gives the highest degree of interaction by the student.
The course includes simulations and the contents are transmitted through the use of educational games to keep the student motivated.
- Basically involves all of the elements of levels 1, 2, and recharged interactivity; and greater levels of sophistication.
- For technical courses i.e. Equipment’s/device explanation, walkthrough, 3d views, hands-on practice, software simulations where a High level of interactivity is required to engage users or disseminate knowledge
- 3D MODELING, 3d Animations, and Video recording, editing shooting comes in level -3


